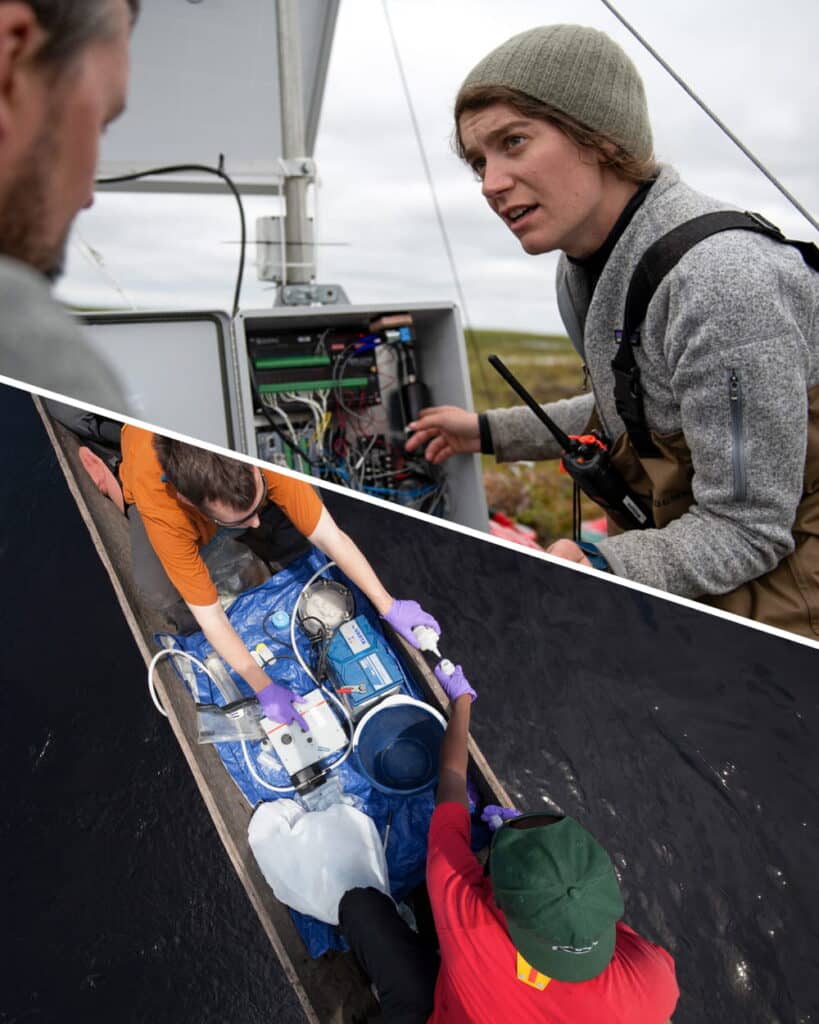
Twelve women carrying the flame for climate action despite the headwinds
It’s been a tough year for anyone working on the climate agenda. The Trump Administration’s repeal of the endangerment finding, the legal underpinning of U.S. climate regulation, was a coup de grace, after a litany of regulatory cuts and other moves to remove any impediment to unfettered fossil fuel development in the world’s largest economy.
Where the U.S. has led, much of the world has followed, with action on the nature and climate crises losing steam as corporate and government leaders have been forced to respond to a new U.S. administration determined to up-end the collaborative, rules-based international order.
What changes for climate targets when permafrost emissions are included?
Permafrost and temperature targets
Permafrost, the permanently frozen ground found in large parts of the Arctic and boreal regions, holds enormous amounts of carbon, roughly twice as much as is currently in the atmosphere. As permafrost thaws, it releases carbon dioxide and methane to the atmosphere and adds significantly to further warming. Permafrost thaw is happening faster and faster and is no longer an issue of the distant future. The potential magnitude of permafrost carbon emissions means they directly affect estimates of remaining carbon budgets needed to keep Earth’s temperature increase below the 1.5° and 2° Celsius thresholds established by the Paris Agreement.
Thanks to the generosity of the Woodwell donor community, the first round of 2026 Fund for Climate Solutions (FCS) awardees has been announced. The FCS supports innovative, solutions-oriented climate science through a competitive, cross-disciplinary process. With more than $10 million raised to date, donor support has already fueled 84 research grants and leveraged millions of dollars in additional research grants since the program’s launch in 2018.
This most recent round of grants is supporting Woodwell experts working directly with communities to generate climate insights, bringing quality data on landscape carbon to international policy venues, and investigating links between climate change and winter weather.
Tracking water quality and empowering communities in the Amazon’s Arc of Deforestation
Lead: Allie Cunningham
The Kayapó people, Mẽbêngôkre (“People of the Water Hole”), are internationally recognized for their leadership in stewarding more than 9 million hectares of intact Amazon rainforest within a region known for rampant deforestation. This territorial defense is coordinated through the Kayapó Project (KP), an alliance of three Indigenous nongovernmental organizations which provides holistic governance and supports Kayapó communities with border patrols and community monitoring systems. Despite this extraordinary stewardship, a critical scientific gap persists, and KP has invited Science on the Fly and Woodwell Climate to help fill it. This FCS-supported project will establish a territory-wide, Indigenous-led scientific platform for water quality monitoring. Woodwell researchers and Kayapó community members will then use the baseline measurements taken to identify threats to the Xingu river ecosystem and Kayapó lands to understand other potential long-term, collaborative community science research.
Red Hook Climate Resilience Partnership: A collaborative initiative to strengthen community preparedness and adaptive capacity to climate risks
Lead: Dr. Nigel Golden
Climate change is making extreme weather events more intense across New York City, but some communities experience greater impacts than others. Red Hook, an area burdened by environmental, social, and economic inequities, was also one of the hardest-hit neighborhoods during Superstorm Sandy—floodwaters reached nearly every block. Despite state initiatives and city resilience plans, residents say their needs continue to be overlooked, and their voices go unheard. Through a partnership between Resilient Red Hook, Woodwell, and CUNY John Jay College of Criminal Justice, residents are leading the charge to change that. With community members as co-researchers, the team will assess climate risks at the neighborhood level and use the assessment to identify adaptation opportunities, with a focus on equity. With the partnerships, baseline data, and findings generated through this work, the team will be able to compete for larger, multi-year grants that can support real action on Red Hook’s terms. The project will also produce a research and engagement framework that other community-science partnerships can draw on.
From Arctic greenhouse gas budgets to policy: An opportunity to translate science to action
Lead: Dr. Bethany Sutherland
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) has a well-recognized issue: its carbon accounting focuses on emissions and uptake due to human activity, without adequately considering natural lands. The Arctic region, which stores vast amounts of carbon, is a critical part of this accountability gap—many regions in the Arctic are already shifting to become net carbon emitters and emissions are projected to continue to rise. Previous Woodwell research has generated carbon budgets for the Arctic by evaluating modeled emissions against observations. With this FCS funding, the project team will amplify those findings and bring Arctic carbon budgets to international policy venues, including the Global Carbon Project and the UN’s Global Greenhouse Gas Watch. The grant will support travel to visit partner institutions and conferences, as well as a workshop hosted at Woodwell. In-person collaboration will strengthen the team’s connections with the global carbon accounting and reporting efforts that inform UN decision making.
Assessing the carbon cycle health and risk of global rangelands systems
Lead: Dr. Jennifer Watts
Rangelands’ soils and plants store large amounts of carbon, and millions of people directly depend on the goods and services these lands provide for well-being and survival. Rangeland ecosystems are also threatened by warming temperatures and land degradation, for example through overgrazing. However, the impacts of these changes on rangeland carbon is poorly understood, and science-informed data hasn’t been available to guide decision makers. The project team will model where rangelands are releasing or storing carbon, and where those lands are at heightened risk from future climate change impacts. This work will produce actionable insights for land management and policymaking at local, regional, and global scales. The team will also present their results at an official side event of the UN Convention to Combat Desertification, representing Woodwell at the conference for the first time.
Hot blobs, cold blobs, and crazy weather: How are greenhouse-gas-fueled SST anomalies affecting Northern Hemisphere weather patterns?
Lead: Dr. Jennifer Francis
Climate change is causing shifts in regional ocean temperatures—both heating and cooling—as the water absorbs extra heat trapped by greenhouse gases while accelerated melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet adds buoyant fresh water to the North Atlantic. When differences in temperature between ocean regions change, wind patterns shift, affecting the jet stream and weather. This project will use artificial intelligence to compare patterns in sea surface temperature and winter weather regimes over North America as well as the North Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Recognizing and understanding how changing ocean temperatures are affecting weather patterns will improve seasonal weather forecasting and help decision-makers prepare for increasingly extreme weather conditions.
Why this US cold snap feels bone-shattering when it’s not record-shattering

The brutally frigid weather that has gripped most of America for the past 11 days is not unprecedented. It just feels that way.
The first quarter of the 21st century was unusually warm by historical standards – mostly due to human-induced climate change – and so a prolonged cold spell this winter is unfamiliar to many people, especially younger Americans.
Because bone-shattering cold occurs less frequently, Americans are experiencing it more intensely now than they did in the past, several experts in weather and behavior said. But the longer the current icy blast lasts – sub-freezing temperatures are forecast to stick around in many places — the easier it should become to tolerate.
There are few things that can lift the heads of the busy Toolik scientists away from their work. But on certain weekdays, behind the maze of dark green storage containers-turned-laboratories, a soft plume of fragrant smoke rises. The tell-tale sign of the awakening Toolik sauna never fails to pull a relieved smile from weary scientists. “Sauna tiiiime,” they whisper underneath their breath, while others let loose a shrill “Yesssssss!” as we hurry to finish the last task of the day. This wooden oasis, tucked into a slope leading into Toolik Lake, is one of the most beloved features of the Toolik Field Station—and a vital community space shaped by the art of storytelling.
On sauna nights, scientists saunter over to the edge of the station, towels draped around our necks. Walking into the mud room, we brace ourselves for the stifling heat we are about to enter. As we walk into the wall of heat we grimace, and then slowly let our shoulders loosen, opening our lungs to the heat—eyes closed, breath heavy, body relaxed.
There is a gentle silence at the beginning of every sauna session as we settle into the damp heat of the room. But soon, conversations start to flow and meander, the sauna filling with the sound of overlapping chatter. People lament their torn-up hands from readjusting rusty bars, muse over the absence of darkness, and fiercely debate the proper name for fish nests (the conclusion, “redds”). I listen to the tale of a soil scientist, swearing that she nearly joined a pack of wolves on a recent data-collection trek. We weigh the strange dependency of this climate research station on the road that was built to expand oil production. And I listen as an older scientist, one who has been coming to Toolik for almost thirty years, recounts how much he has seen this landscape, which he has come to love so deeply, change so much.
In these moments, I cannot help but think, “This is what it’s all about.” Scientists—across disciplines, countries, generations—sharing the weight and joy of their lives of work. An ecologist’s work, not unlike the heat that we choose to sit in every time we walk through the sauna’s doors, can be heavy and at times, suffocating. But under this pressure, in these spaces of relaxation and healing, we inspire celebration, reflection, and resolution with the stories we tell.
We bask in our love for science— a shared love for adventure, mystery, the land, and a dedication to protect and heal it.
For younger scientists, listening to the stories of older scientists bends time, reminding us of what has been lost—and the urgency with which we must continue to defend these changing ecosystems.
Once we leave the sauna, these stories become incredibly special tools. Global change can be insidious, its effects hiding beyond our daily lives. But by sharing these stories, we have the power to reach out and envelop others in our world, finding that perfect heartstring to tug.
We need people working from every angle, from both within and beyond the scientific community, to understand, mitigate, and adapt to the consequences of our rapidly changing world. And while the Toolik sauna is an incredibly unique ecosystem of human beings, sweat, and laughter, I—and many of my fellow scientists—happily hold the responsibility of disseminating the words that are shared in that space with all of our communities so that everyone can take a turn basking in the sauna at the top of the world.
Woodwell Climate Research Center to expand soil carbon testing capacity
Woodwell Climate Research Center, in Falmouth, is getting an $800,000 federal earmark to develop a dedicated soil carbon research lab.

We hear a lot about carbon stored in oceans, trees, and of course the atmosphere. But there’s about three billion tons of carbon stored in soils around the world, according to Jonathan Sanderman. He’s a senior scientist and vice president of science at Woodwell Climate Research Center, in Falmouth.
Our salmon are vanishing — and the State of Alaska is letting it happen

I live along the Yukon River, where my family has harvested salmon for countless generations. Every summer used to bring the same reassuring sight: Busy fish camps. Full smokehouses. Families coming together to pass down traditions that have thrived for thousands of years. Happy kids, curious babies, loving grandparents, moms, dads, aunties, uncles and cousins. Each is an intrinsic part of a beautiful summer day at the smokehouse.
Today, summers mean less time on the river, empty smokehouses and fish camps, and no intergenerational learning. The State of Alaska tells my community and over 50 other Indigenous communities in Alaska and Canada that we are the ones who must stop fishing, we are the ones who must sacrifice, we are the ones who must somehow bear the burden of a crisis we did not create.
Continue reading on Alaska Beacon.
Are stratospheric polar vortex disruptions what they seem?

A weak or distorted stratospheric polar vortex (SPV) is often associated with severe winter weather in Northern Hemisphere continents. Traditional metrics of the SPV state, however, may conflate influences from both the stratosphere and the troposphere below, obfuscating attribution of weather extremes. In a new paper, published this month by Climate Dynamics, researchers present a new method that more clearly separates variations in the two atmospheric layers and their contributions to severe winter weather.
Depending on your feelings toward cold and snow, the headline “The Polar Vortex is Coming!” may instill dread or delight. The Polar Vortex first entered dinner-table conversations during the extreme winter of 2013/14, the coldest North American winter of the 21st century, and has since been used—often incorrectly—as shorthand for any cold or snowy spell. The polar vortex is a pool of frigid air encircled by strong westerly winds that sits high above the polar regions during winter only, and normally it has little influence on weather at the surface. But when it becomes disrupted from its typically circular shape—either stretched to an oblong, split into separate swirls, or greatly weakened—extreme winter weather can ensue, including severe cold, snow, and even winter heat waves.
One of the ways scientists track the behavior of the stratospheric polar vortex is to monitor the height of a constant pressure surface that exists within the stratosphere. Pressure decreases at higher altitudes because there are few air molecules above that level. The height of a pressure surface bulges and shrinks depending mainly on the temperature of the air below it: warmer air expands and cooler air contracts. Height fluctuations of a level in the stratosphere, then, are caused by temperature changes in the whole column of atmosphere below that level, not only in the stratosphere. Disruptions to the SPV detected using pressure heights, therefore, may be misleading as to their cause.
“As I explored the role of stratospheric disruptions on extreme winter weather, it occurred to me that there might be a better way to measure those disruptions,” said Dr. Jennifer Francis, Senior Scientist at Woodwell Climate Research Center and lead author. “Focusing on the stratosphere itself rather than the whole atmospheric column helps separate the influences from the two layers, which often behave independently.”
The authors analyzed the thickness of a layer in the stratosphere using an AI-based approach to identify representative patterns in the SPV, including various types of disruptions.
“The new metric revealed an increased occurrence of strong and abnormally cold SPV patterns,” added co-author Natasa Skific, Researcher at the Woodwell Climate Research Center. “This is different from findings in earlier studies based on pressure heights. Our findings make sense because higher concentrations of greenhouse gases cool the stratosphere, causing a stronger SPV.”
Paper co-author Dr. Judah Cohen, Research Scientist at MIT Parsons Lab and Director of Seasonal Forecasting at Atmospheric and Environmental Research, noted the previously underappreciated common occurrence of vortex stretching, which often contributes to cold spells in the U.S. and central Eurasia.
“The results of our study fit with other work highlighting the importance of stretched-vortex states on severe winter weather. Our new metric helps isolate the stratosphere so we can better understand its dynamics and connections with weather extremes, atmospheric blocking, and amplified Arctic warming.”