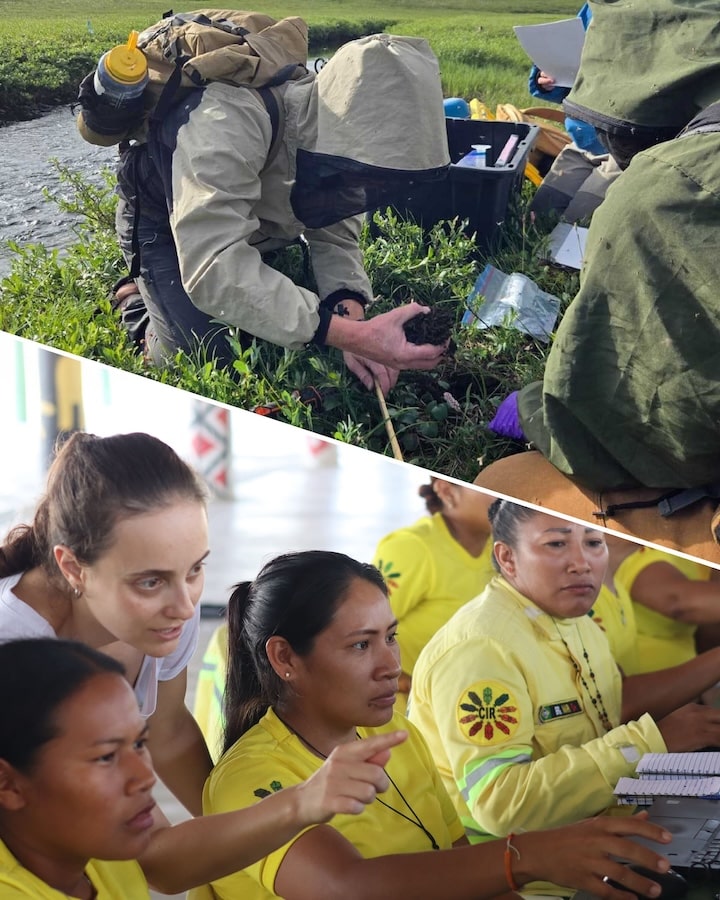
A map of Alaska created by Senior Geospatial Analyst Greg Fiske garnered two awards—the International Cartographic Association and International Map Industry Association Recognition of Excellence in Cartography, and Cartography Special Interest Group Excellence—at the Esri User Conference in San Diego this week.
Esri is the industry leader in mapping software and the Esri User Conference brought together more than 20,000 geospatial professionals including cartographers, software developers, students, end users, and policymakers. Woodwell Climate has an ongoing partnership with Esri and has attended the conference for more than two decades.
“These awards mean a great deal as the recognition comes from two very highly acknowledged cartographic organizations and the map pool at the Esri User Conference was immense,” Fiske said. “In the case of this map, not only did I share a basemap that we’re using widely in our Permafrost Pathways project, but I also shared a high-level overview of how I created the map and the resources (in the format of data, software, tutorials, and people) needed to do the same anywhere on the planet.”
The map that won the awards shows the topography of Alaska. To the average viewer, it is beautiful, informative, and not overly complicated. But Fiske also created a storymap that breaks down the data layers, and analytical and design steps required to create the map—and it is anything but simple.
Fiske has been creating maps at Woodwell Climate for more than 20 years, and is known among colleagues—at the Center and across the mapping community—for his analytical skill, creativity and artistry, and dedication to quality.
“People are drawn to a beautiful map,” Fiske said. “Putting our work on a map takes advantage of that scenario and gives us an opportunity to spotlight our research.”
6 women leading the fight against climate change
Following in the footsteps of climate pioneer Eunice Newton Foote, these six women are making strides in the fight against climate change with support from Google.org.
Eunice Newton Foote was the first woman to publish in a physics journal. Her article, titled “Circumstances Affecting the Heat of Sun’s Rays,” laid the foundation for the discovery of the greenhouse effect. This groundbreaking paper, written more than 150 years ago, drew a direct link between carbon dioxide and the warming of our climate, and helped define climate science as we know it. Today, on her 204th birthday, we’re honoring her achievements with a Doodle on the Google homepage.
We’re also celebrating the work of six women walking in Eunice’s footsteps and making important contributions to our understanding of climate change. With funding and support from Google.org, these innovators are working to educate the public, building solutions to mitigate the effects of climate change and advocating for policies that will help protect our planet.
On July 17, 2023, Woodwell Climate Research Center announced $5 million in grant funding and a Fellowship from Google.org, the tech company’s philanthropic arm, to support the development of a new, open-access resource that will use satellite data and artificial intelligence (AI) technology to make it possible to track Arctic permafrost thaw in near real-time for the first time.
As the Arctic warms at nearly four times the global rate, permafrost—or ground that has remained below 0 degrees C for at least two consecutive years–that underlies much of the region is thawing rapidly, causing widespread ground collapse and infrastructure damage, threatening Arctic communities, and releasing carbon into the atmosphere. To date, real-time analysis of permafrost thaw has been out of reach due to the limitations of remote sensing and satellite imagery analysis. This new resource—an expansion of the Permafrost Discovery Gateway (PDG)—will use AI technology to streamline the data analysis process and make it easier to rapidly identify patterns and trends in permafrost thaw datasets that will be essential to informing climate mitigation and adaptation strategies.
“Timely tracking of permafrost thaw is critical to assessing impacts and informing action, but current limitations in technology, combined with the rapid pace of change in Arctic landscapes, have held us all back,” said Dr. Anna Liljedahl, Woodwell Climate Associate Scientist and project lead. “This project will be groundbreaking in speeding up data analysis and unlocking completely new technological capabilities in how we do science in swiftly evolving landscapes, and, ultimately, what science itself can do.”
“Nonprofits have told us that when they use AI, they’re able to reach their goals in a third of the time and at half the cost,” shared Brigitte Hoyer Gosselink, Director of Product Impact at Google.org. “The thawing of arctic permafrost is a timely issue the world needs to better understand so that we can take collective action. Google.org is proud to support Woodwell Climate Research Center to conduct permafrost thaw analysis in near real-time; work that is now possible thanks to advanced technology like AI.”
The grant is being given to Woodwell Climate Research Center as part of Google.org’s Impact Challenge on Climate Innovation, a $30M commitment to fund big bet projects that accelerate technological advances in climate information and action. In addition to funding support, Google.org will offer access to Google’s products and the support of a Google.org Fellowship, a pro bono program that matches Google employees—engineers, user experience designers, program managers and more—with nonprofits and civic entities for technical projects, full time for up to six months.
The three-year effort, being undertaken in partnership with University of Connecticut; National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis, University of California Santa Barbara; National Center for Supercomputing Applications; Arizona State University; Alfred Wegener Institute; University of Alaska, Fairbanks; and Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium, will focus on building automated workflows for geospatial product creation, AI models capable of identifying changes, patterns and trends, as well as environmental and climatic drivers, tera to petabyte scale permafrost thaw datasets.
In particular, the technology will enable scientists, decision makers, community members, and other interested groups and individuals to explore permafrost thaw features that formed during the previous month, check out seasonal forecasts of permafrost thaw, predict disturbance events based on weather forecasts, estimate carbon and infrastructure loss from abrupt permafrost thaw, and analyze the shape and size of permafrost thaw features and their patterns across the landscape over time. This resource will also be applicable beyond the scope of permafrost thaw, enabling experts to adapt this technology for other research areas and expand access to key climate data and actionable insights across a range of issues and regions of the world.
“Permafrost, often perceived as a distant phenomenon in the remote North, has broad impacts on the world that are yet not fully understood. The Arctic Data Center looks forward to preserving and sharing pan-Arctic permafrost datasets for anyone looking to find and utilize them for scientific research,” said Matthew Jones, Director of Informatics R&D at National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis, University of California Santa Barbara. “Using this data, we collectively have the opportunity to understand the intricate and cascading effects of permafrost on a global scale and influence the trajectory of mitigation programs.”
“We will unlock the strengths of sub-meter resolution commercial satellite imagery and AI to create pan-Arctic scale geospatial map products of permafrost landforms, thaw disturbances, and human-built infrastructure” said Chandi Witharana, Assistant Professor, University of Connecticut and project partner.
“We are excited to be working with Google.org to improve and extend the tools and data pipelines initially developed for the Permafrost Discovery Gateway (PDG) to new use cases. Closing the time gap between remote sensing data products becoming available and permafrost data products being published, such as the pan-Arctic sub-meter scale ice-wedge polygon dataset developed by Chandi Witharana and team, will hopefully help scientists and stakeholders better understand permafrost thawing at the pan-Arctic scale. We also hope to generalize some of the technologies and tools being developed so that more scientists can leverage this work to develop new permafrost related data pipelines,” said Luigi Marini, Lead Research Software Engineer at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA).
“It is great when we can connect researchers and teams such as NCSA’s scientific applications team, so that partnerships can develop to further scientific discovery,” stated Laura Herriott, Associate Director for Research Consulting at the NCSA. Herriott is also on the leadership team of Delta, co-PI on the new DeltaAI system, and co-PI for the Advanced Cyberinfrastructure Coordination Ecosystem: Services & Support (ACCESS) program. Computing resources offered by the National Science Foundation via Delta and the ACCESS Allocations supported the development of the pan-Arctic ice-wedge polygon dataset, which is published today and available to explore on the PDG.
“As a geospatial scientist and an AI researcher, it is really exciting to have the opportunity to develop cutting-edge geoAI to advance Arctic science, to inform climate actions and influence policies,” said Wenwen Li, Professor at Arizona State University and project partner. “I look forward to collaborating with our wonderful team to develop physics-informed, AI-based discovery tools that incorporate big, spatiotemporal data to identify new patterns, areas of rapid changes, and make forecasts on permafrost dynamics. Permafrost Discovery Gateway will host our new findings and tools and make them publicly accessible.”
“Permafrost is a central clock wheel in the complex mechanisms driving the ecological changes resulting from climate change—in the arctic and in the rest of the world. The Permafrost Discovery Gateway will couple the strengths of high spatio-temporal remote sensing information and Machine Learning to advance our understanding of the resilience and vulnerability of permafrost to climate change across the landscape. As an ecologist and a modeler, I cannot wait to leverage this new information to develop predictive tools of permafrost thaw disturbances, and their impacts on the landscape, the carbon cycle and the global climate system.” said Hélène Genet, Associate Professor at the Institute of Arctic Biology at the University of Alaska Fairbanks.
“Permafrost covers a huge region of the northern hemisphere land mass and its disappearance either by gradual thaw but also by rapid thaw and erosion processes will fundamentally contribute to global climate change,” said Guido Grosse, Head of Permafrost research at Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine research, and project partner. “New geospatial methods and data processing techniques employed in this project jointly with experts from around the world will provide a first highly detailed look at permafrost thaw and its consequences at the pan-Arctic scale.”
“Once frozen and resilient, the Arctic is transforming into a landscape that is thawing and fragile. The Permafrost Discovery Gateway is a resource that communities can use to access data, explore climate change impacts, and find resources to adapt in healthy ways,” said Michael Brubaker, Director of Community Environment and Health at Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium.
The effort will also collaborate with and provide more accurate, timely, and complete information to Permafrost Pathways, a major initiative also led by Woodwell Climate, funded through the TED Audacious Project and in partnership with the Arctic Initiative at Harvard Kennedy School and the Alaska Institute for Justice. “This funding through Google.org will allow us to take permafrost carbon modeling to the next level by including abrupt thaw and integrating AI solutions into the estimations of permafrost carbon losses, enabling us to monitor threats to infrastructure in near-real time, estimate future risk, and inform planning to help us better respond to and prepare for permafrost hazards in Alaska communities and beyond” Liljedahl says.
More information about this project can be found here: blog.google/outreach-initiatives/google-org/google-permafrost-thaw-tracking
Heavy rain to become more frequent with climate change, experts say: ‘We’re heading into a new normal’
These once-in-100-years severe climate events are now likely to occur once every 37 years, data show.

Four days last week were recorded as the hottest days on Earth in modern history, with the global average temperature reaching 17.23 degrees Celsius, or 63.01 degrees Fahrenheit.
Then came the rain. Storms pummeled New England and millions were placed under flood watches through Massachusetts, New York, and Vermont. The torrential rain has been compared to the likes of Hurricane Irene, with residents being evacuated from homes and vehicles. One fatality has been reported in New York.
Read more on The Boston Globe.
Climate change keeps making wildfires and smoke worse. Scientists call it the ‘new abnormal’

It was a smell that invoked a memory. Both for Emily Kuchlbauer in North Carolina and Ryan Bomba in Chicago. It was smoke from wildfires, the odor of an increasingly hot and occasionally on-fire world.
Kuchlbauer had flashbacks to the surprise of soot coating her car three years ago when she was a recent college graduate in San Diego. Bomba had deja vu from San Francisco, where the air was so thick with smoke people had to mask up. They figured they left wildfire worries behind in California, but a Canada that’s burning from sea to warming sea brought one of the more visceral effects of climate change home to places that once seemed immune.
“It’s been very apocalyptic feeling, because in California the dialogue is like, ‘Oh, it’s normal. This is just what happens on the West Coast,’ but it’s very much not normal here,” Kuchlbauer said.
Continue reading on Associated Press.
Scorching heat and Canada wildfires could be tied to ‘wavy, blocky’ jet stream
Some researchers think climate change is disrupting the jet stream’s flow and causing it to bake regions in heat longer.

Scientists say a closely watched atmospheric pattern — the jet stream — is behind both the Canadian wildfires and the scorching heat in Texas, raising questions about how it shapes extreme weather events and whether climate change is disrupting its flow.
The jet stream, a ribbon of air that encircles the Northern Hemisphere at high altitudes, drives pressure changes that determine weather across North America. The jet stream’s wavy pattern creates areas of high and low pressure.
‘Never occurred before’: How the Arctic is sizzling Texas

The oppressive heat wave roasting Texas and Mexico is rekindling a scientific debate about the effects that Arctic climate change might have on weather patterns around the world.
Many experts say that rapid warming in the Arctic — where temperatures are rising four times faster than the global average — may cause an increase in these kinds of long-lasting extreme weather events.
Canada’s wildfire season is off to an ‘unprecedented’ start. Here’s what it could mean for the US

Raging wildfires in Canada have already scorched about 15 times the normal burned area for this time of the year: nearly 11 million acres — more than double the size of New Jersey — with more than 2 million acres concentrated in Quebec alone.
Canada’s fire season is only just beginning, and officials there warned this week it would continue to be severe through the summer. If it follows the pattern of a normal year, it will peak in the hotter months of July and August.
But this is anything but a normal year.