Success or failure? Woodwell scientists deem COP26 a mixed bag
Glasgow Climate Pact alone is not enough to limit warming to 1.5 C, but COP26 made real progress

Hanging globe above the main stage at COP26.
photo by Beth Brazil
For the first two weeks of November, diplomats and scientists from around the world descended on Glasgow, Scotland for the United Nations’ 26th annual Conference of Parties—hailed by some as the “last, best, hope” for successful international cooperation on the issue of climate change. Woodwell sent three expert teams to push for more ambitious policies that integrate our understanding of permafrost thaw and socioeconomic risks, and for financial mechanisms to scale natural climate solutions. Here are their thoughts on the successes and failures of this pivotal meeting.

CONSERV panel with (l-r) Marcela Paranhos (IDH), Marcelo Stabile (IPAM), Glenn Bush (Woodwell), and Jenny Xie (Wellington).
photo by Anneka Williams
Bold pledges but uncertain follow-through for tropical forests
The conference started off with a bold promise from 100 nations to end deforestation by 2030, accompanied by a pledge of more than $19 billion from both governments and the private sector. Though similar pledges to end deforestation have failed in the past, the funding pledged alongside this one gives reason to be hopeful.
$1.7 billion of the funds are allocated specifically to support Indigenous communities, which Woodwell Assistant Scientist Dr. Glenn Bush believes is a big step forward, though creating policies that are equally supportive will be where the real work gets done.
“It’s particularly welcome that Indigenous peoples are finally being acknowledged as key protectors of forests. The real challenge, however, is how to deliver interlocking policies and actions that really do drive down deforestation globally and scale up nature-based solutions to climate change.”
Dr. Ane Alencar, Director of Science at IPAM Amazônia, said that, for Brazil, half of the solution could come from enforcing existing laws and designating public forests. The other half could come from consolidating protected areas, creating incentives for private land conservation, and providing technical support for sustainable food production.
Dr. Bush also presented the CONSERV project, a joint initiative between IPAM and Woodwell that provides compensation for farmers who preserve forests on their land, above and beyond their legal conservation requirements. Increasing the scale and financing of viable carbon market plans like CONSERV could be crucial in incentivizing greater forest protection.

Risk panel with (l-r) Dr. Elena Manaenkov (WMO), Thandie Mwape (IFRC), Dr. Katharine Hayhoe (Nature Conservancy), Nick Bridge (UK Special Rep), and Dr. Li Zheng (Tsinghua University).
photo by Natalie Baillargeon
Climate risk a growing focus for governments
During the second week of the conference, Woodwell released a summary report on a series of climate risk workshops with policymakers and climate risk experts from 13 G20 nations. These workshops, conducted in collaboration with the COP26 Presidency and the British government’s Science and Innovation Network, identified challenges to incorporating climate risk assessments into national-level policy, and the report made recommendations for moving from simply making the science available to making it useful for implementation. The report demonstrated a desire from policymakers to get involved in climate risk analyses early in the process, to ensure the information addresses a country’s particular needs.
One success of the conference was the creation of a new climate risk coalition, led by Woodwell. The coalition, composed of 9 other organizations, will produce an annual climate risk assessment for policymakers.
“Understanding the full picture of climate risk is incredibly important when you’re setting policy,” explained Woodwell’s Chief of External Affairs, Dave McGlinchey. “We also heard, however, that the climate risk assessments need to be designed with the policymakers who will eventually use them. This research must speak directly to their interests if it is going to be delivered effectively.”
The increased desire of policymakers to better understand and address oncoming climate risks demonstrates an important shift to viewing climate change as a present problem, rather than solely a future one.
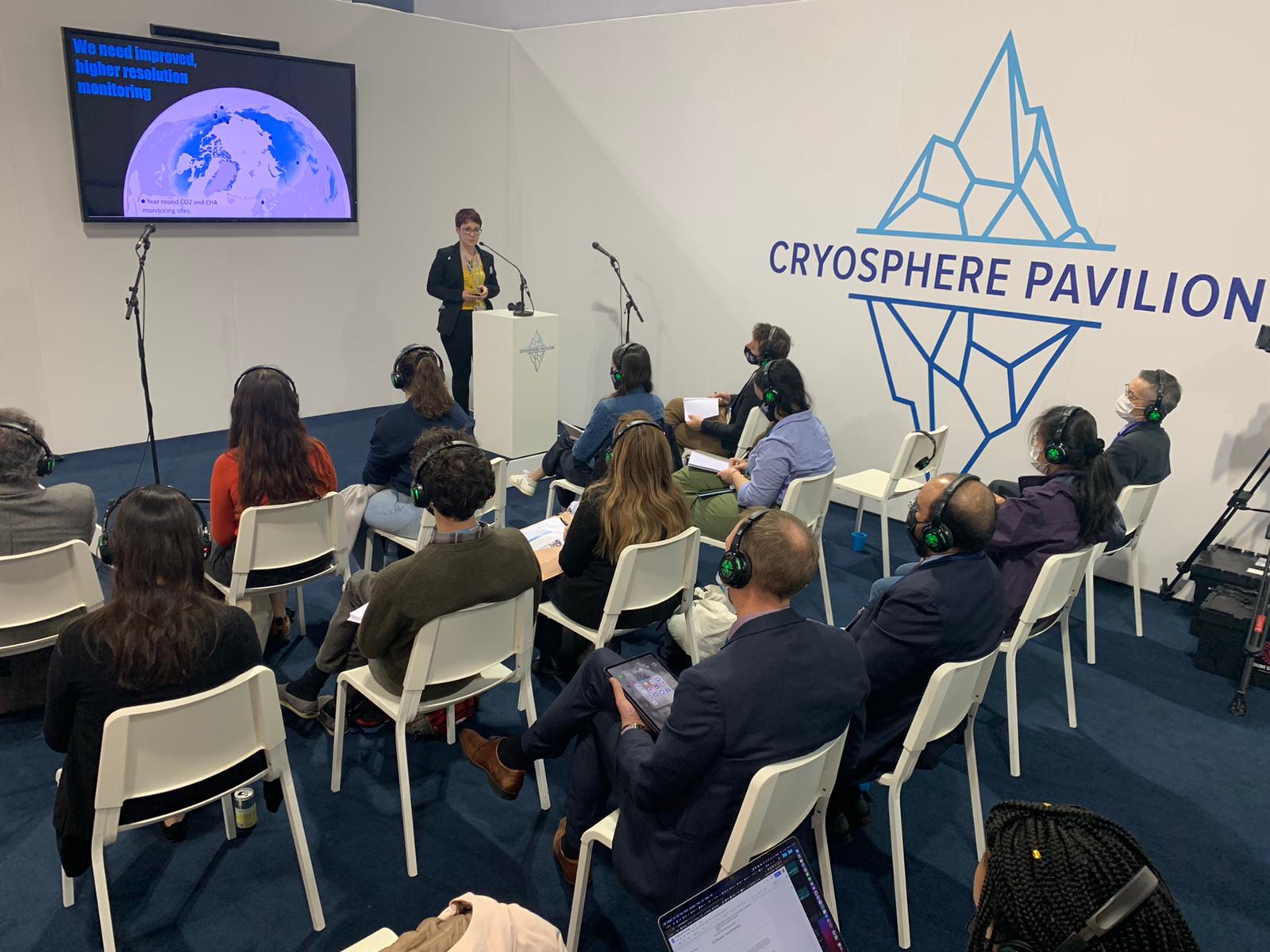

Dr. Rachel Treharne presents in the Cryosphere Pavilion.
photo by Dave McGlinchey
Permafrost thaw presents the greatest remaining uncertainty in forecasting emissions
One risk that still isn’t high enough on the COP agenda is rapid Arctic change, particularly permafrost thaw. The Cryosphere Pavilion, hosted by the International Cryosphere Climate Initiative, convened conversations ranging from the implications of permafrost thaw, to environmental justice for Northern Communities and respecting Indigenous knowledge and culture. For Arctic Program Director, Dr. Sue Natali, the Indigenous-led panels were some of the most impactful of the conference. But postdoctoral researcher Dr. Rachael Treharne noted that, no matter how well attended, there’s a difference between being in the Cryosphere Pavilion and being on the main stage.
Woodwell was among a group of organizations pushing to get permafrost emissions the attention it demands. Emissions released by thawing permafrost are currently not accounted for in national commitments, but are potentially equivalent to top emitting countries like the U.S. November 4 at the conference was “Permafrost Day” and each event was at full capacity for the pavilion, signaling growing attention to permafrost science. Woodwell, alongside a dozen polar and mountain interest groups called for even more commitment to the cryosphere conversation at the upcoming Subsidiary Body for Scientific and Technological Advice U.N. climate conference in Bonn scheduled for June of 2022.
Even with this greater recognition of the seriousness of Arctic climate change, the region and its people are being hit much harder and faster than the rest of the globe. Slow-moving decision-making and talk without follow-through will seriously endanger Arctic residents.
“I left the COP having a very hard time feeling ‘optimistic’, while knowing that the hazards of climate change are already severely impacting Arctic lands, cultural resources, food and water security, infrastructure, homes, and ways of living,” said Dr. Natali. “After repeated years of record-breaking Arctic wildfires, heatwaves, and ice loss, I’m not sure how a 1.5 or 2C warmer world—one in which we know that these events will only get worse—is a reasonable goal.”
Though missing necessary milestones at COP26, climate action is accelerating
Overall, however, the final Glasgow Climate Pact fell short of the ambitious action the world needs in order to limit warming. The deal made several last-minute compromises surrounding the phase out of fossil fuels. COP president Alok Sharma said that, while a future with only 1.5 degrees of warming is possible, it is fragile—dependent on countries keeping to their promises.
Despite this, McGlinchey says there was real progress at COP26. The conference reached a resolution that earned the unanimous agreement of all attending parties. The formal process has also begun to accelerate, with nations required to return with more ambitious climate mitigation plans next year, rather than on the previous five year timeline.
“We are not yet where we need to be,” McGlinchey said. “But we are better off than where we were two weeks ago. Let’s keep going.”